GILSONITE IN DRILLING FLUIDS
GILSONITE IN DRILLING FLUIDS
GILSONITE IMPROVES DRILLING EFFICIENCIES, WELLBORE STABILITY, FILTER CAKE DEVELOPMENT AND MORE.
As an integral component of premium drilling fluid products, Gilsonite actively improves drilling efficiencies while reducing costs and minimizing the HSE impact associated with most drilling fluid additives.
Gilsonite is the only drilling fluid additive that provides all of these benefits:
Gilsonite prevents formation damage
Gilsonite forms a physical and chemical bond with permeable formations, creating an effective seal to prevent the passage of drilling fluid. By uniquely functioning as both a malleable and solid plugging agent, Gilsonite controls fluid loss and seepage, prevents lost circulation and protects reactive and low-reactive shale surfaces, even at elevated bottomhole temperatures.
Proven to strengthen the wellbore
HP/HT wells, shales and underpressured zones require specialized drilling fluids and wellbore-strengthening techniques. Adding Gilsonite to an OBM, SBM or WBM strengthens the well by:
The most effective additive to prevent differential sticking
Gilsonite minimizes the occurrence of stuck pipe and stuck logging tools by thoroughly sealing permeable formations – even in zones with a highly overbalanced pressure differential – and improving filter cake lubricity.
We bellow briefly explain the drilling muds
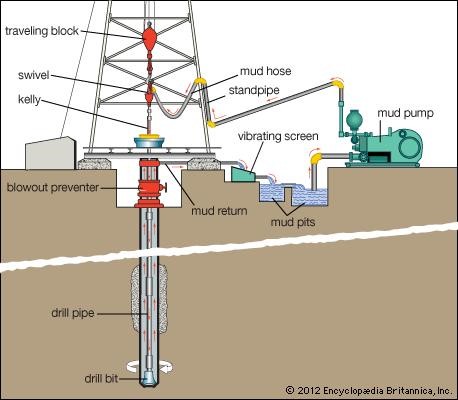
Drilling mud, also called drilling fluid, in petroleum engineering, a heavy, viscous fluid mixture that is used in oil and gas drilling operations to carry rock cuttings to the surface and also to lubricate and cool the drill bit. The drilling mud, by hydrostatic pressure, also helps prevent the collapse of unstable strata into the borehole and the intrusion of water from water-bearing strata that may be encountered.
Drilling muds are traditionally based on water, either fresh water, seawater, naturally occurring brines, or prepared brines. Many muds are oil-based, using direct products of petroleum refining such as diesel oil or mineral oil as the fluid matrix. In addition, various so-called synthetic-based muds are prepared using highly refined fluid compounds that are made to more-exacting property specifications than traditional petroleum-based oils. In general, water-based muds are satisfactory for the less-demanding drilling of conventional vertical wells at medium depths, whereas oil-based muds are better for greater depths or in directional or horizontal drilling, which place greater stress on the drilling apparatus. Synthetic-based muds were developed in response to environmental concerns over oil-based fluids, though all drilling muds are highly regulated in their composition, and in some cases specific combinations are banned from use in certain environments.
A typical water-based drilling mud contains a clay, usually bentonite, to give it enough viscosity to carry cutting chips to the surface, as well as a mineral such as barite (barium sulfate) to increase the weight of the column enough to stabilize the borehole. Smaller quantities of hundreds of other ingredients might be added, such as caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) to increase alkalinity and decrease corrosion, salts such as potassium chloride to reduce infiltration of water from the drilling fluid into the rock formation, and various petroleum-derived drilling lubricants. Oil- and synthetic-based muds contain water (usually a brine), bentonite and barite for viscosity and weight, and various emulsifiers and detergents for lubricity.
Drilling mud is pumped down the hollow drill pipe to the drill bit, where it exits the pipe and then is flushed back up the borehole to the surface. For economic and environmental reasons, oil- and synthetic-based muds are usually cleaned and recirculated (though some muds, particularly water-based muds, can be discharged into the surrounding environment in a regulated manner). Larger drill cuttings are removed by passing the returned mud through one or more vibrating screens, and sometimes fine cuttings are removed by passing the mud through centrifuges. Cleaned mud is blended with new mud for reuse down the borehole.